In this guide, you’ll learn the best SEO tips for beginners. It includes real examples and actionable advice to help you understand the basic SEO rules.
As a beginner to search engine optimization (SEO) you need to understand that there is no magic way to rank your website on the first page of Google, Bing or Yahoo.
Search engines are governed by complex algorithms and it takes a lot of time and effort to ‘convince’ them that your website or web page deserves one of the top spots.
Nevertheless, there are certain rules you can follow to optimize your website and provide the search engine bots with the necessary signals.
While the web is floated with SEO tips and advice, most of the articles talk about SEO at a theoretical level and not how SEO can be applied in practice.
In my opinion, this is why most website owners are confused and either they give up with SEO or simply do not get the expected results.
What you will read in this post is SEO advice that works.
I have tested this strategy over the years on a number of websites with remarkable results.
Google SEO Tips for Beginners
The most important SEO tips that can make a difference to your Google rankings are:
- Optimize your page titles and meta descriptions
- Create SEO friendly URLs
- Add a breadcrumb menu to your internal pages
- Add internal links to your content
- Use headings and formatting options to make your pages easier to read
- Customize your 404 page
- Optimize your images
- Improve your page speed
- Get backlinks from other websites
- Make sure that your website is mobile-friendly
- Create an XML sitemap and a User sitemap
- Improve the quality of your content
- Update your website with fresh content
- Check for broken links
- Use Google webmaster tools and analytics
Of course, there are many other things you can do to help your website achieve better rankings, but the SEO tips presented below will give you a solid and reliable framework that is 100% safe (i.e. without taking any risks of getting a Google Penalty) and above all, it works.
In addition to the tips, I have added real examples from two web sites that I’ve been doing SEO work, to help you understand how to apply the guidelines on your own website or blog.
1. Page Titles and description
Page titles
Page titles are a very important aspect of SEO and this is why it is the first item on my list.
My findings for the last couple of months showed that page titles are more important than ever especially for Google SEO.
The most important characteristics of an optimized page title are:
- Each page needs to have a unique page title that accurately describes the page’s content.
- Be brief and descriptive.
- Help the user understand what the page is about
Home page title: The title for your homepage can include the name of your website/business and other bits of important information like the physical location of your business or maybe a few of its main focuses or offerings.
The titles of other posts/pages of your website should accurately describe what the page is about and be attractive to the searcher.
Description
The page description meta tag is also very important. It gives users, Google, and other search engines a summary of what the page is about.
Google may choose to show what you type in the description as a snippet for your page or may decide to use a part of your page’s content.
In other words, it does not mean that what you write in the description will show in the snippet.
The guidelines for writing a good meta description are:
- Always provide a unique description for all pages, posts, products of your website.
- Keep the meta description length between 180-200 characters.
- Avoid repeating the title in the description
- Don’t add too many keywords
- Try to use the description as a way to ‘advertise’ your page to the reader so that they click on your title and visit the page.
2. Permanent link structure
The permanent link structure is a term used to describe the format of URLS for pages (categories/tags) or individual posts of a web site.
It is shown in the browser address bar and in the search results (below the page title).

Guidelines for SEO Friendly URLs
- Make Urls simple and easy to understand for search engines and users
- Use hyphens ‘ – ‘ to separate the words that make up a URL
- Avoid lengthy Urls with unnecessary information
- Use words that describe what the page is about but avoid keyword stuffing
Examples of BAD URL structures
- http://www.example.com/UK/123213/5005.html
- http://www.example.com/socialmedianews
- http://www.example.com/id=7&sort=A&action=70
Examples of GOOD URL structures
- http://www.example.com/social-media-news
- http://www.example.com/2002/12/social-media-news
3. Breadcrumb
Make sure that you have a breadcrumb trail on all your internal pages. A breadcrumb is a set of links at the top of the page that aid navigation. If you are using WordPress there are many free plugins to create a breadcrumb.

4. Internal links
When we talk about internal links we mean links in a page that point to other pages within the website i.e. not external links.
In the example below, when you click on the link with anchor “increase the intensity” you will be redirected to a page with-in the website to find out more information on how to increase the intensity of an exercise.
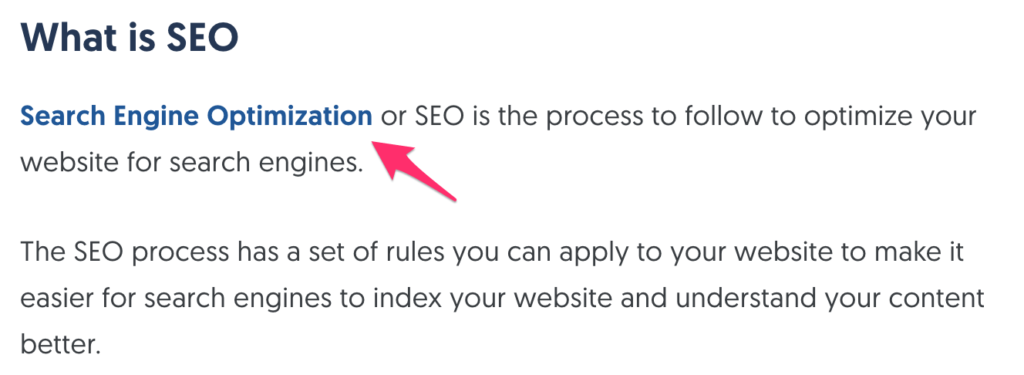
Internal linking is a very important factor for website SEO but still many web site owners are not using it correctly. The rules to follow for internal links are simple:
- Link related articles together either by using keyword anchor text or by using the full article title.
- Make sure that the links are useful both for the user and easy to understand by search engines.
- Don’t make links for search engines only. An internal link should help the user navigate the site better.
- Do not use terms like ‘click here’ or ‘[..]’ for internal linking.
- Don’t overdo it. A few internal links per page are enough (create more if really necessary)
Pro Hint: Don’t always link old posts from new posts but every couple of weeks go back and link newer posts from older posts.
It’s not an easy task to do especially if you have a lot of posts but it’s a very valuable tool for on-site SEO.
5. Text formatting and the use of H1, H2, and H3
Don’t just publish pieces of text on your website without first doing some basic formatting. This is not good for the user experience and works against your SEO efforts.
General guidelines for formatting a post or page on your website:
- Use H1 tags for the title of your post
- Use H2 tags for the main headings of your post.
- Use BOLD and Italics to draw users attention
- Don’t use H2 tags for all your headings
- Write small paragraphs
- Use a font size that is easy to read
When formatting your posts always have in mind the user experience. Can the user identify the main sections of your post (H2 tags) just by looking at the page? Is the text easy to read on all devices (smartphones, Apple Ipads, Android tablets, etc)?
6. The 404 Page
SEO is about improving the user experience and a proper 404 page contributes to that goal.
The 404 page is the page shown when a user is looking for a page on your site that doesn’t exist or mistypes a URL or follows a broken link. When the 404 page is not configured, it looks like this:
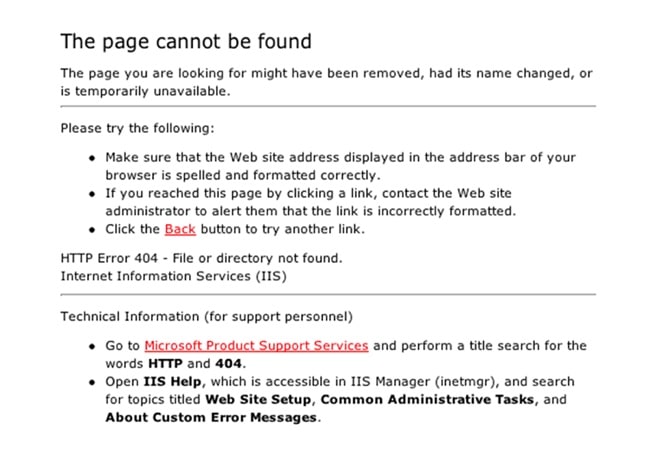
This is not useful for the user and negatively impacts the user experience.
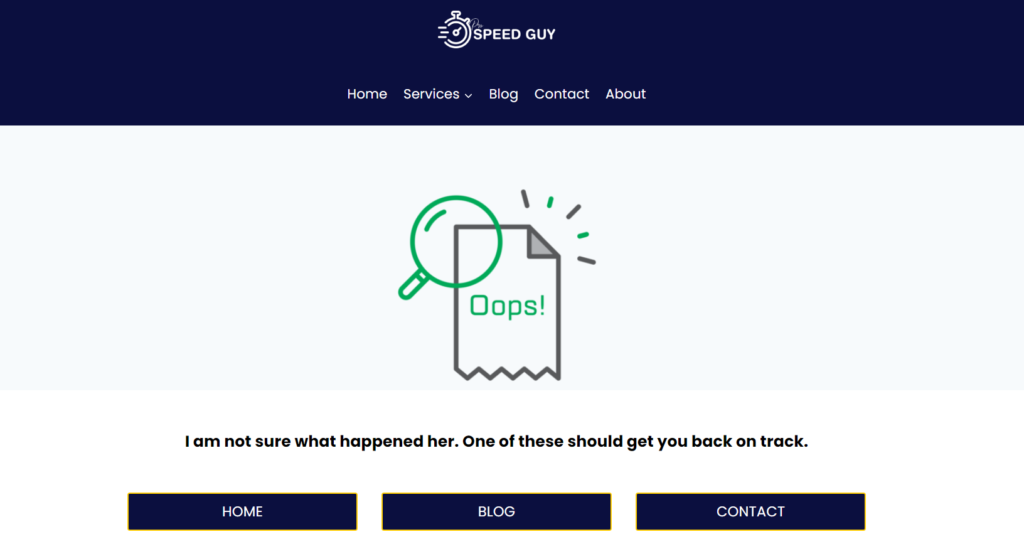
A properly configured 404 page should:
- Give some info to the user of what happened rather than displaying “Not found”
- Have a design consistent with the rest of the website
- Give options to the user to navigate to other pages of the site.
This is how my 404 page looks like:
7. Image Optimization
Images are necessary to enhance the user experience but care should be taken not to create other side effects like problems with page load speed or slow response.
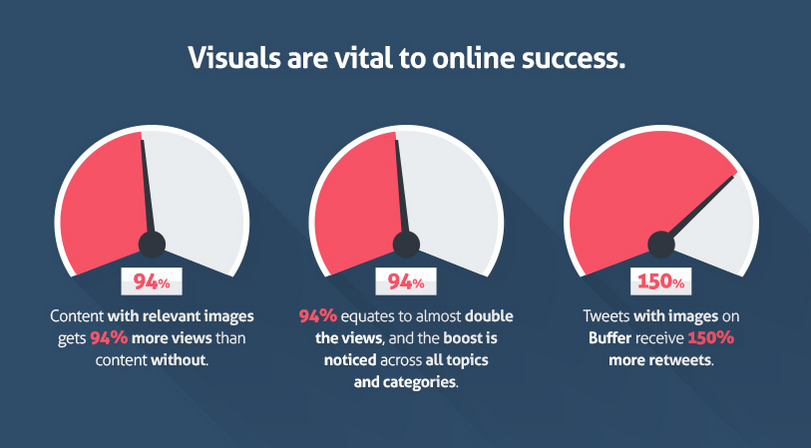
If you decide to use images, mind the following:
- Use Alt Text to describe the image. You can add keywords but don’t overdo it.
- Use keywords in image filenames (separated with dashes). Avoid using filenames like image1.jpg or person1.jpg. Instead, use meaningful names with dashes. For example woman-working-out.jpg
- Keep all image files in a dedicated folder in your site i.e. www.mydomain.com/images/
- Optimize the image size. The smaller the size of the image (in KB) the faster your website will load.
8. Page Speed
Google mentioned many times that page speed is a ranking factor and yet many webmasters don’t optimize their web sites for speed. Their aim (Google’s) is to provide the searcher with the most accurate results in the fastest possible way.
It is certain that page speed (as a ranking factor) will gain more importance in the next couple of years.

Fast web sites improve the user experience and it is a factor to encourage the visitor to come again. In addition, a website that loads in less than 4 seconds is more likely to:
- Rank better in search results
- Get more page visits per user
- Get more conversions
How to tackle the page speed problem?
- Remove any unnecessary plug-ins (if you are using WordPress) or javascript from your pages.
- Optimize the size of your images.
- Use a caching service or plug-in.
- Go to http://www.webpagetest.org/ and test how many seconds it takes for your pages to load from different locations, internet speed, and browsers. The analysis report at the end will also tell you which components of your page take too long to load so that you can remove them.
- Go to Google Page Speed Service to analyze your web site and get performance recommendations.
- If you have a lot of images on your site and you cannot improve performance with the recommendations given by the tools mentioned above you can consider using a CDN (Content Delivery Network) service such as Cloudflare or Amazon Cloud Front
I know that tackling issues related to performance is a technical issue and sometimes it’s not easy for the average user to identify and solve the problems.
Nevertheless, it is a very important factor for SEO and should not be neglected.
9. Get Links from Other Websites
There is no way to avoid mentioning link building when we talk about SEO. The reason is simple: Off-Page SEO factors play a very critical role in the Google ranking algorithm.
I know that for beginners to SEO this is a concept difficult to understand, so let’s take it from the beginning.
What is link building and why it is very important for SEO?

When Larry Page and Sergey Brin (Google Founders), created the initial Google ranking algorithm, they were looking for a way to compare websites so that the best were shown first in the search engine results pages (SERPS).
Besides taking into account the on-page SEO factors of a page, they decided that websites that have incoming links from other websites are probably more important and popular than others, so they deserved a better ranking.
In other words, incoming links counted as ‘votes of trust’ and this had a positive effect on a website’s ranking position. The more incoming links pointing to a website the better was the ranking position.
In the beginning, this was something that could easily be manipulated. Webmasters who understood this concept started building thousands of links pointing to their websites and increased their rankings.
The problem was that some of those websites were not good quality websites and they did not actually deserve to be on the first page of Google. Over time this created a huge problem for Google that impacted the quality of their search results.
To protect their reputation and keep spam websites away, Google started adding more strict rules to their ranking algorithm and they were able to differentiate between natural and artificially created links.
The result was a success for Google. Spam and low-quality websites did not only lost their rankings but in many cases, they were removed from the Google index.
This was the time that Google penalties became more popular and words like Panda and Penguin (that’s the name given to Google ranking algorithm changes) became a nightmare for many webmasters.
To sum up this introduction to link building, you should understand 3 things:
1st -> Links are still a very important aspect of SEO.
2nd -> It’s no longer a matter of quantity (how many links are pointing to your website) but of quality (from where these links are coming).
3rd ->Natural links are good for your rankings, artificially generated links can get you into trouble.
How to approach link building (the safe way)
So, it should be clear by now that links are important, but how do you get them?
Link building is a huge topic, but I will outline below the most important elements:
- Publish great content on your website that will naturally attract links
- Put your content in front of other webmasters/bloggers that may potentially link to your website (Facebook and other social media channels are great promotion tools for this purpose)
- Link to other websites and reach out to webmasters informing them that you added a link to their websites. If they like your website, they may return the favor – This is actually advice given by Google in one of their guides.
- Publish content on other websites and add links pointing to your pages (this is also known as guest posting)
- Make connections with other webmasters and let them know about your website (twitter and email are great tools to built connections with other people)
- Try to get links from high-quality websites only
- Get links from websites related to your niche and not any kind of website
- Built your link profile gradually (any sudden changes to the number of incoming links may raise some warnings signals in the ranking algorithm)
- Make sure you understand the difference between a ‘follow’ and ‘nofollow‘ link
- Read Google’s guidelines on link building
- How you approach link building for new websites is different than older websites so make sure that you use the right techniques
- Use tools like SEMRUSH to analyze the link profiles of your competitors and try to learn as much as you can about their link practices
- Check your link profile frequently and take action if necessary to clean your profile from unwanted links

Link building mistakes to avoid:
- Don’t buy links (avoid any sort of link building packages)
- Don’t do any form of massive link building
- Don’t add your link in low-quality websites
- Links from comments or forums can sometimes do more harm than good (unless they are genuine and from well-trusted sources)
10. Mobile-friendly web sites
A significant number of searches performed each day are through mobile devices. Many studies over the last 6 months identified that the number of searches using smartphones is steadily increasing especially when it comes to making online purchases.
I am sure that if you take a look at your analytics data you will see a good percentage of your daily visits coming from mobile.
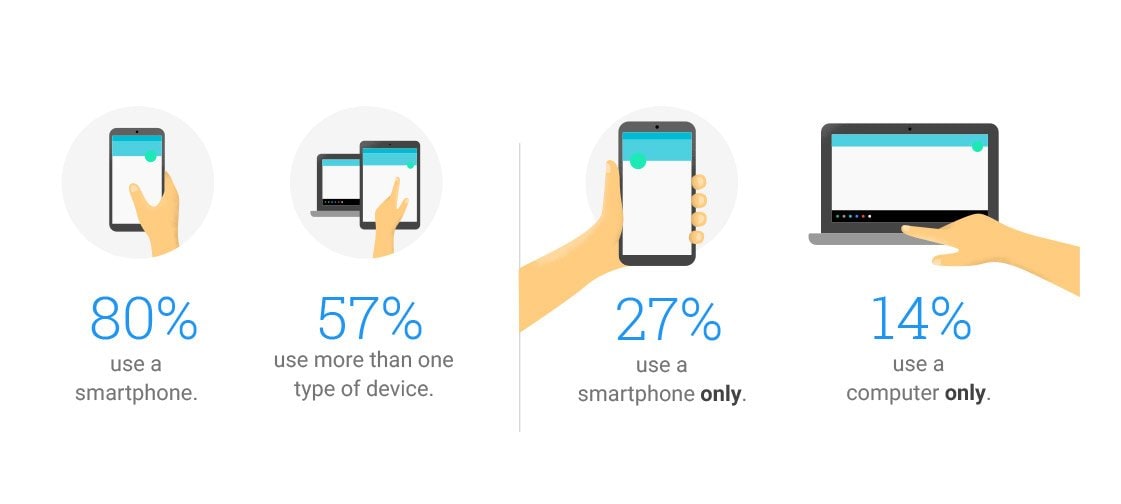
It’s not in the scope of this post to go in detail into mobile SEO but there some simple steps to follow to ensure that your website is mobile-friendly.
- The first thing to do is understand the difference between a mobile-friendly web site and a native Android, iPhone or Windows Mobile app. After talking with a number of webmasters I realized that many people fail with their mobile strategy because they do not understand this difference and because they have not yet realized the enormous potential of mobile markets.
- A mobile-friendly web site is optimized for viewing on the mobile browser (i.e. Chrome on android or Safari on iPhone). A native android (iPhone or Windows Mobile app) is an application that can be downloaded from the mobile markets (Google Play or Apple Store). I will cover this with more details in another post but for SEO purposes you must provide a mobile-friendly version for your users coming through mobile browsers.
Update: The best way to approach Mobile SEO is to adopt a responsive website design. There are many advantages both in terms of SEO and usability.
11. User Sitemap
A sitemap is a list of all posts/pages of your website. You need 2 types of sitemaps. First, an XML sitemap to submit to Google, Bing and other search engines and second an HTML sitemap to help visitors find your content easier.
It is recommended to place a link to your user sitemap from the main menu.
XML Sitemap (for search engines)
Depending on your blogging platform you can use plugins to create and update your website’s sitemap. When viewed in the browser it looks like this:
HTML Sitemap (for Users)
The user sitemap should provide links to all (or to the most important pages of your site). It can also group posts by author, date, category, etc. Its purpose is to help the user find information on your site easier and quicker. My user sitemap looks like this:

12. Content is still king
In order for the above tips to work you need first and foremost to have good content on your web site.
Content is still king and a web site with good, original, quality content can do better in the long run (with or without SEO) than a web site optimized in SEO but with not so good content.
What is good content?
When people search on Google, Yahoo or Bing they are essentially looking for an answer to a question. Good content is a post or page that answers this question.
How do I know if my content is good?
There are two simple ways to understand if your content is useful.
First, you can check your analytics and especially the time users spent on a page. A reader will stay longer on the page if the content is good and second the number of social media shares (Facebook likes, tweets, etc.).
This is actually a very good way to understand what users want and what type of content to provide on your website or blog.
How to write good content?
There is no simple answer to this question, but the following guidelines can put you in the right direction:
- Make sure that your content delivers what promised in the title. If for example, your title is “How to lose 15 pounds of fat” make sure that your post provides an accurate description (or steps) that someone can follow to achieve the desired result.
- Check your text for typos, spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Format your text (as explained in Tip 8 above)
- Provide links within your content (where appropriate) to other pages on your site (or other sites) to get more information.
- Include references from established research or studies (where appropriate) to prove that what you are saying or suggesting is correct.
Quantity VS Quality
Many people often ask me “How long (in words) should I make my posts?” You should understand that there is no single answer that fits all purposes. It greatly depends on the type of post and topic.
For example, the post you are reading now is more than 4000 words because it is a vast topic. In order to explain to someone the basic rules of SEO, I had to make the post that long.
If for example, you are writing about the benefits of black chocolate then surely you won’t have to write that much.
This is exactly where quantity vs. quality comes into place. It’s better to write a quality post without counting words rather than a long unfriendly post for the sake of providing more word count.
Google’s official view about content length is very clear: Short content can be useful and rank well.
What does Google consider good content?
A couple of weeks after the release of Penguin, Google published a set of criteria for accessing the quality of a web site. Among the suggested guidelines they included some questions to ask after you finish a post, to help you determine the quality of your work.
13. Fresh Content
Having fresh content is an incentive for visitors to come back and for search engine bots to visit and crawl your website more often.
This is true when you really have something new to say about the niche or topic your covering. Avoid publishing pages with similar content just for the sake of updating your web site or blog.
14. Check your external links
External links (links in your web site pointing to other sites) are important for SEO. In general ensure that:
- You are not linking to spam web sites or web sites with inappropriate content
- You have no broken links i.e. links to web sites or pages that no longer exist (you can use xenu – a free tool to analyze your external links).
- You are not in any way selling or exchanging links
- Any links in your comments section carry the nofollow directive
15. Webmaster tools and Analytics
Google and Bing have what is called webmaster tools. This is the place to register and submit your web site to their index.
After submission, you can visit the webmaster central and get valuable information about your web site.
Although this is not directly related to SEO, when you submit your web site to Google search console and Bing webmaster tools you gain a number of advantages:
- It’s a way to tell search engines about your web site (by submitting your sitemap)
- It’s a way to get feedback on the number of pages indexed
- It’s a way to get notified about potential problems i.e. access issues that restrict web sites from crawling your content
- You can see the number of incoming and internal links.
Also, it is very important to use Google Analytics (or any other traffic analysis tool) to:
- Find out how visitors find your web site (direct visits, search, referrals, etc)
- How much time they spend on your pages (and on which pages)
- What keywords they used
- How many pages they view per visit
Bonus Tips:
Schema Markup
One of the ways to help search engines understand the context of your content is through the use of structured data markup. In simple terms, structured data is a way to annotate your content so that crawlers can index your pages better.
Although this is not officially part of the Google ranking algorithm, it is something that can improve the presentation of your pages in the search results and this means higher click-through rates and more organic traffic.
There are various schemas for almost all kinds of content (articles, videos, images, products, etc) and websites (personal, business, local business, etc).
Canonical URLs
Canonical URLs are very important for SEO. Setting a canonical URL for all your pages is a great way to:
- Avoid duplicate content issues
- Consolidate links to a particular page (this is useful for eCommerce websites or websites with dynamic URLS with parameters).
- Tell Google the original publisher of an article in case you syndicate your content on other websites.
I have followed all the above SEO Tips, now what?
Once you have optimized your website for SEO by following ALL of the above guidelines, the next steps are:
Concentrate on improving your web site by (proving more content, whether it’s new product info, articles, services – or whatever you are trying to achieve).
Promote your web site using techniques that work and above all are safe.
If you fail with your SEO optimization your web site may not be running on its full potential but if you follow wrong promotion techniques you increase the risk of getting a penalty and completely destroy your efforts.
